Better Family Article Series
Liquid Multivitamins
The Absorption Advantage
This article series is brought to you by the team behind Liquid Daily: the better option for filling nutritional gaps in your household.
Liquid Is Better
Simplify Your Routine
You're In Control

Article Highlights
- The main distinction between these two deliveries lies in how medications are absorbed into the bloodstream: sublingually or orally.
- The sublingual route is characterized by placing a drug under the tongue, enabling direct absorption into the bloodstream.
- Liquid Daily, as one of the best liquid multivitamins for adults, provides a balanced combination of vital nutrients that may be lacking in a typical diet.
Sublingual Vs. Oral
Sublingual vs. oral administration is a topic that has garnered much attention in healthcare and pharmaceuticals. The main distinction between these two deliveries lies in how medications are absorbed into the bloodstream: sublingually or orally. Understanding this difference is crucial to determining the most suitable approach for a specific medication.
The sublingual meaning comes from the Latin words “sub” (under) and “lingua” (tongue), describing how the method works. A sublingual tablet, for example, is designed for rapid absorption and placed under the tongue to dissolve. This absorption occurs through the mucous membranes lining the floor of the mouth, allowing direct entry into the bloodstream and bypassing the need to pass through the digestive system and liver in a process known as first-pass metabolism. This process can significantly alter or reduce drug concentration.
Alternatively,
Comparing sublingual absorption vs. oral absorption warrants consideration of the advantages and disadvantages of both methods. Sublingual administration offers a rapid onset of action due to its direct access to circulation. It is especially beneficial in emergencies like angina pectoris or acute pain relief, which constitutes a time-sensitive treatment. Additionally, bypassing first-pass metabolism ensures a higher bioavailability for certain drugs that can otherwise be extensively metabolized orally. However, not all drugs are suitable for sublingual delivery because of factors like taste and solubility in saliva, which can limit their use. In contrast, oral administration is often considered more convenient and user-friendly, with the added advantage of a wider range of available dosage forms like tablets, capsules, and liquids.
"So happy not to have to swallow big pills ever again."
- Jeff H.
Start feeling better with Liquid Daily - the liquid multivitamin packed with 18 essential nutrients & vitamins.
TRY LIQUID DAILYSublingual Administration
Sublingual administration is an often-overlooked but highly effective method of drug delivery. This administration method has been garnering attention in various medical and pharmacological fields. The sublingual route is characterized by placing a drug under the tongue, enabling direct absorption into the bloodstream through the rich vascular supply in the sublingual mucosa. As a result, sublingual administration bypasses the gastrointestinal tract and hepatic circulation, avoiding first-pass metabolism and leading to rapid onset of action.
The sublingual route has several advantages over other methods of drug delivery. For example, it offers improved bioavailability compared to oral ingestion, as drugs do not undergo degradation in the stomach or intestines. Furthermore, it provides rapid systemic absorption due to the extensive network of blood vessels beneath the tongue. This swift uptake is particularly beneficial in emergencies where quick relief from symptoms is crucial.
One notable application of sublingual administration is treating angina pectoris, a type of chest pain caused by lowered blood flow to the heart muscle. Patients experiencing an angina attack can use nitroglycerin tablets placed under the tongue for immediate pain relief, thanks to this method’s swift absorption into circulation. Another example includes administering opioid analgesics like buprenorphine for managing severe pain or treating opioid dependence. The advantage in this case lies in achieving higher systemic concentrations at lower doses due to reduced hepatic metabolism while being convenient for patients who may struggle with swallowing tablets or capsules.
Despite its benefits, there are some limitations associated with sublingual administration that warrant consideration. Not all drugs possess characteristics suitable for the sublingual route. Substances must exhibit sufficient water solubility and permeability across the mucosal barrier to be effective through this method. Additionally, some medications can cause local irritation when applied directly to sensitive oral tissues, meaning that the sublingual route isn’t suitable for everyone.
Buccal Vs. Sublingual
Buccal vs. sublingual administration of medications is a topic that merits attention and scrutiny, especially in the context of bioavailability and efficacy. These two routes of drug delivery share some similarities but also have distinct differences that may impact patient preference, compliance, and overall therapeutic outcomes. The buccal route involves placing a drug between the cheek and gum, allowing direct absorption through the oral mucosa. This method bypasses the first-pass metabolism when drugs are ingested and absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. Consequently, buccal administration can result in higher bioavailability compared to oral ingestion. In addition to circumventing first-pass metabolism, buccal delivery offers other advantages such as rapid onset of action, ease of use, and less risk of aspiration or choking than swallowing medication.
On the other hand, sublingual administration entails placing a medication under the tongue, where it is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream via the numerous blood vessels in this area. The sublingual route also avoids first-pass metabolism and has a similar bioavailability profile to buccal delivery. Additionally, sublingual dosing allows for swift absorption and rapid onset of action due to its proximity to blood vessels. Like buccal administration, sublingual application is convenient and carries minimal risk of aspiration or choking
When comparing buccal vs. sublingual bioavailability, both methods bypass first-pass metabolism. Still, they may yield different absorption rates depending on factors such as drug solubility, formulation, or even saliva production. In analyzing sublingual vs. buccal drug delivery methods, it’s essential to consider patient-specific factors like comfort level with either technique or the presence of any medical conditions that may preclude one method over the other. For example, patients with oral lesions or inflammation might find buccal administration uncomfortable and prefer sublingual dosing. Certain medications may be more suited to one route than another depending on stability and desired effect.
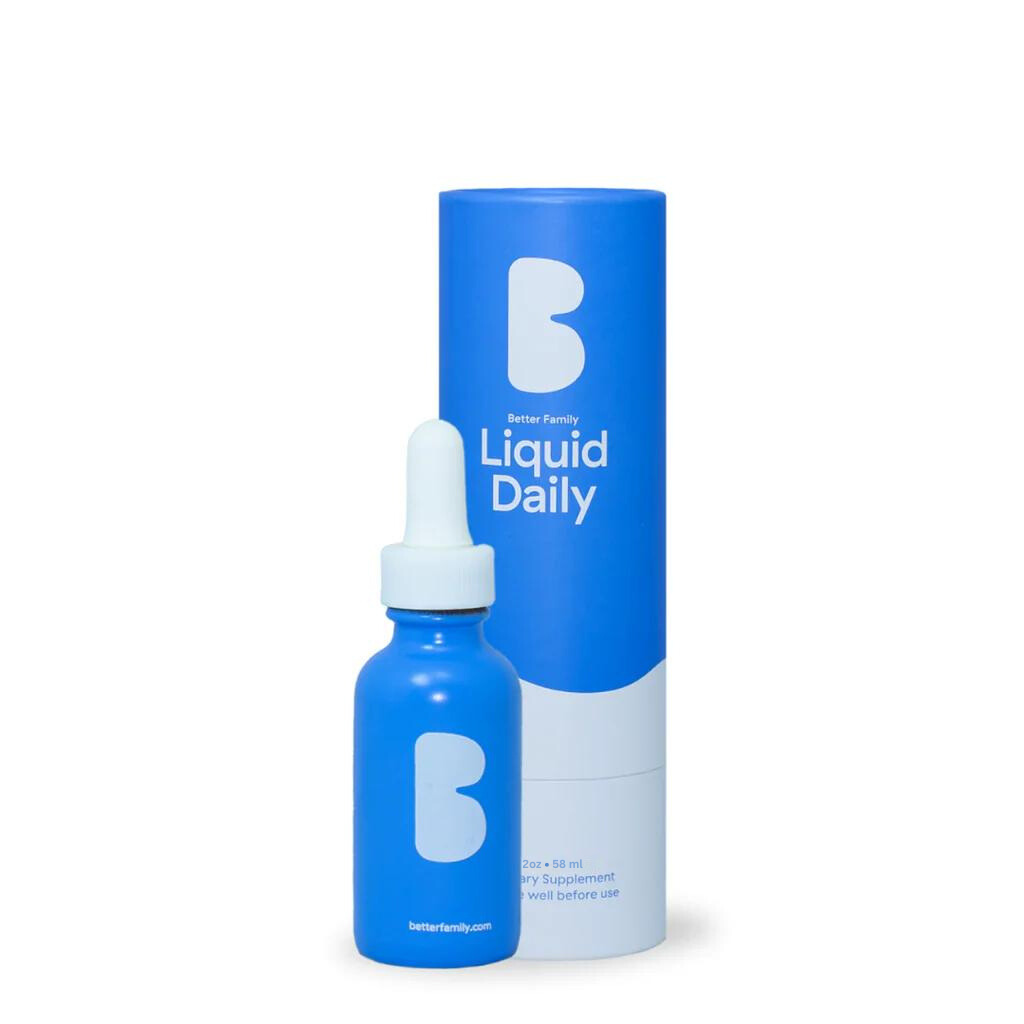
Try Liquid Daily
Liquid Daily is the all-in-one liquid multivitamin that contains the highest quality formats of the most important vitamins and minerals.
- 18 Essential Vitamins & Minerals
- Advanced Liquid Absorption
- Zero sugars, fillers, or artificial flavorings
- Safe & Effective for Kids & Adults!
How to Increase Sublingual Absorption
The fascinating world of sublingual absorption is a unique and efficient method of administering various substances directly into the bloodstream by placing a substance under the tongue to bypass the digestive system and improve bioavailability. Learning how to increase sublingual absorption can significantly enhance the efficacy of certain medications and supplements, leading to improved overall health and well-being.
One aspect worth considering when discussing sublingual absorption is time. Understanding the sublingual absorption time is important to deciding if sublingual administration is right for you. Knowing how long it takes to absorb a substance through this method can provide valuable insights into maximizing its effectiveness. While age, weight, and genetics may influence sublingual absorption time, it typically peaks at 10 minutes. By acknowledging this time, one can optimize their sublingual intake schedule and ensure they are making the most of their chosen supplement or medication.
Numerous techniques can be employed to harness the power of sublingual absorption. First, ensuring the mouth is clean and free from debris or food particles can help maximize contact between the mucous membranes under the tongue and the desired substance. Additionally, using pure compounds with smaller particle sizes can facilitate more rapid absorption by increasing the surface area available for interaction with these membranes. Another useful tip to enhance sublingual absorption involves gently massaging or pressing the area beneath your tongue while holding your supplement or medication in place. This action helps stimulate blood flow within these tissues, encouraging quicker uptake into your bloodstream.
Furthermore, staying mindful of factors like saliva production can also play a vital role in improving sublingual efficacy. By limiting swallowing during the administration of a given substance–especially during those crucial first few minutes–one can essentially “trap” more active ingredients under their tongue, where they are more likely to be absorbed directly into circulation.
Sublingual Route Advantages
Numerous sublingual route advantages have garnered significant attention in recent years, particularly as alternative methods of drug administration. The sublingual route offers numerous benefits over conventional oral ingestion, contributing to its growing popularity. One of the most appealing aspects is its ability to bypass the digestive system, allowing patients to experience quicker and more efficient medication absorption.
Sublingual tablets are a prime example of how this route can offer unique benefits. These tablets are specifically designed for placement under the tongue, where they dissolve in saliva and are absorbed directly into the bloodstream. This process eliminates concerns about gastric irritation or degradation by stomach acid and enzymes. Additionally, sublingual tablets have uses extending to various medications for pain relief, anxiety disorders, and even some cardiovascular conditions.
When considering liquid multivitamins like our Liquid Daily supplement, the sublingual route provides another compelling option for people seeking improved bioavailability. Many individuals may struggle with swallowing large pills or capsules, making liquid formulations a more palatable choice. Users can optimize absorption rates by administering these nutrients via the sublingual route while minimizing potential gastrointestinal discomfort.
Moreover, it’s essential to recognize that certain populations might particularly benefit from the advantages offered by sublingual administration. For instance, individuals with difficulty swallowing or compromised gastrointestinal function may find this method preferable to oral administration in terms of comfort and effectiveness. Furthermore, patients requiring rapid onset of action–such as people experiencing acute pain or anxiety–can benefit from the expedited absorption afforded by this route.
The sublingual route is highly versatile and often advantageous for administering medications and supplements. Its capacity for rapid absorption and avoidance of digestive system obstacles can be especially effective and useful for specific patient populations or conditions requiring swift intervention. As researchers continue exploring novel applications in drug delivery, interest in sublingual administration will continue to grow across various fields.
"Just 2 mL of the liquid held under my tongue for 15 seconds is all I need to know that my body is capturing 60%-70% more nutrients than the capsules and pills I used to consume. "
- Adam C.
Try the lightly and naturally flavored liquid multivitamin - the perfect blend of essential nutrients, including methylfolate.
TRY LIQUID DAILYMore articles from Better Family