Better Family Article Series
Liquid Multivitamins
The Absorption Advantage
This article series is brought to you by the team behind Liquid Daily: the better option for filling nutritional gaps in your household.
Liquid Is Better
Simplify Your Routine
You're In Control

Article Highlights
- Liquid vitamins can be absorbed more quickly than pills and tablets, at an absorption rate of up to 98% compared to the 3%-20% of certain pill and tablet vitamins
- While crushing or dissolving tablet vitamins may increase absorption, it is not recommended as it may result in unwanted dosaging due to the altered format
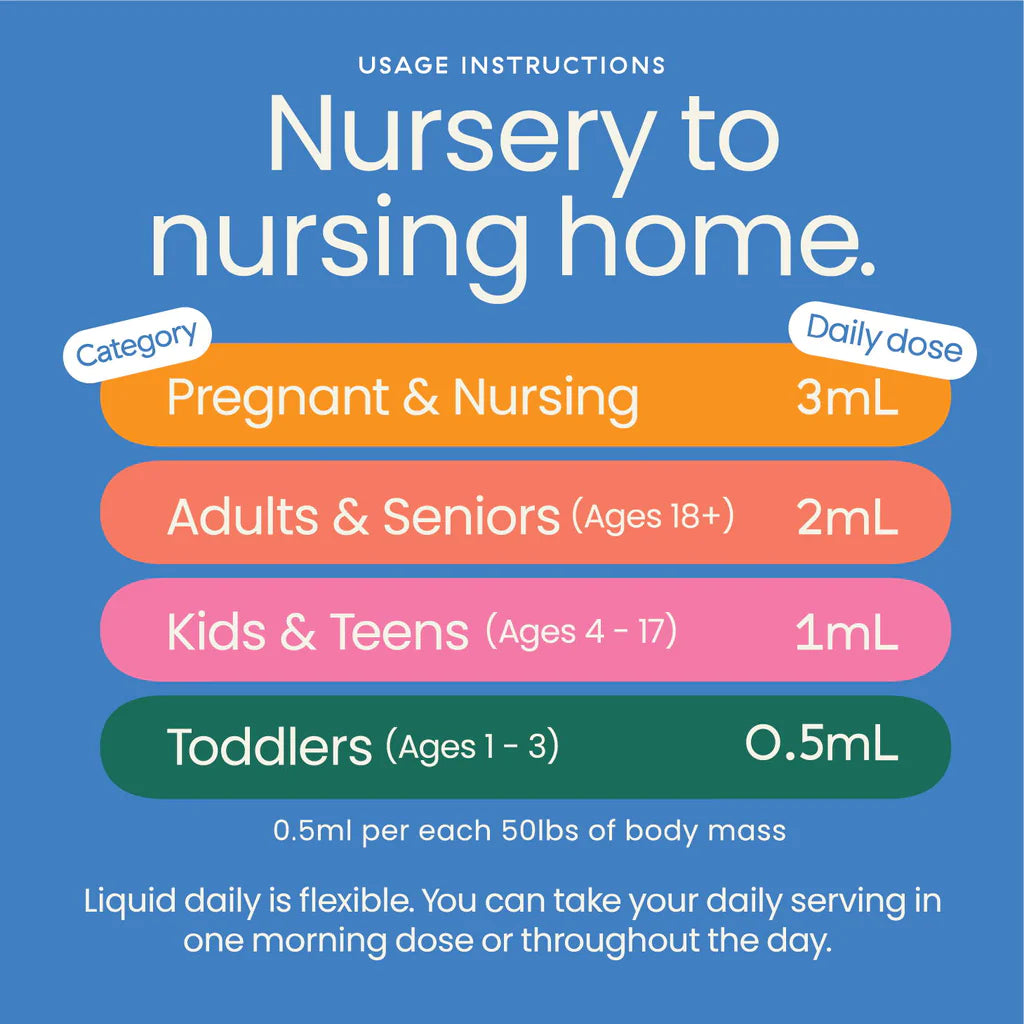
- Starting with a liquid vitamin and taking the recommended amount may be the best option for you
Can You Dissolve Multivitamins in Water?
If you’ve stumbled across this article, chances are you’re curious how to absorb vitamins better. Perhaps you’ve heard that liquid vitamins are absorbed more quickly than pills and tablets (1), at an absorption rate of 98% versus the 3%-20% you’d get from pills (2). That said, you may still have tablets lying around and don’t want to lose out on the investment of the ones you already have. If you’d like to know if you can dissolve multivitamins in water, the answer is yes.
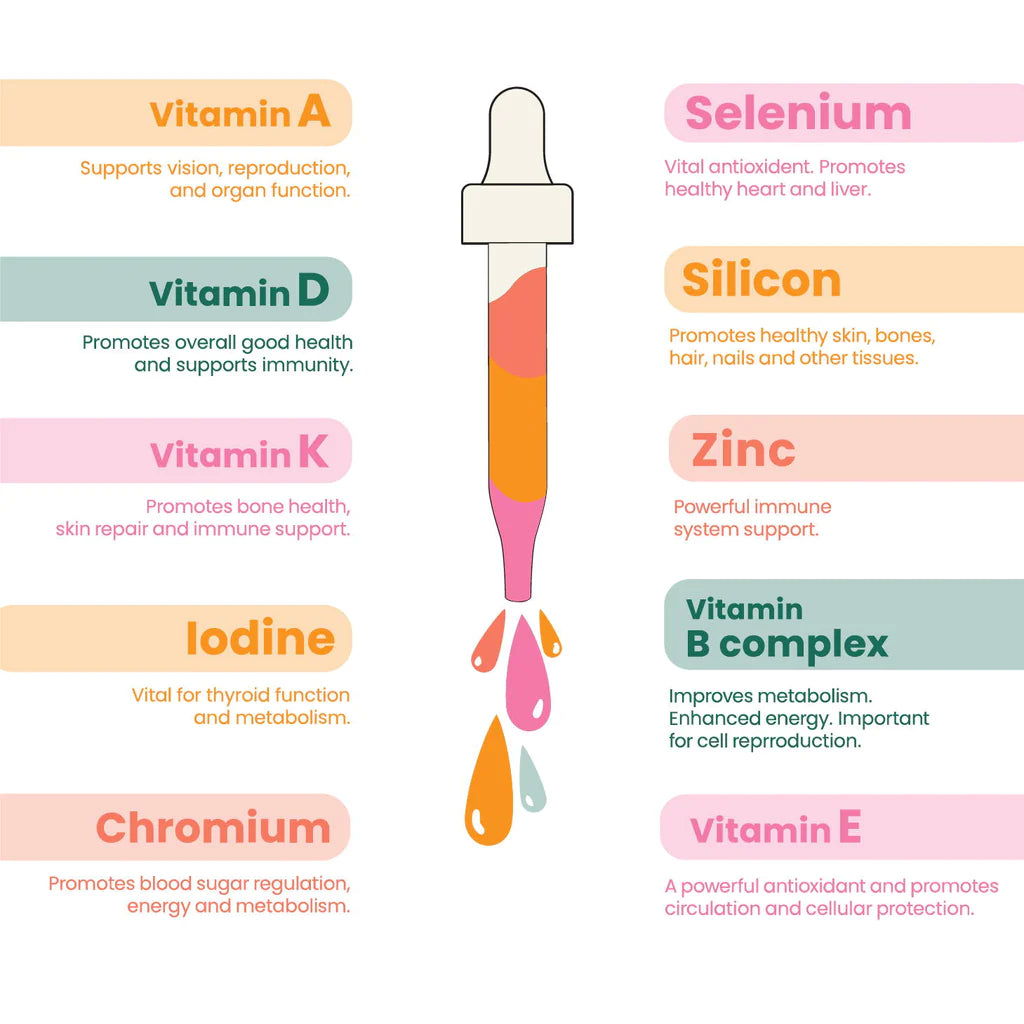
Some vitamins are already predisposed to be dissolved in water. These water-soluble vitamins include B vitamins and vitamin C (3). Vitamin B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B5 (pantothenic acid), B6, B7 (biotin), B9, and B12 (cobalamin) are all water-soluble. These vitamins aren’t stored in your body and should be regularly included in your diet. Fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamin A, D, E, and K (4) should be eaten with a meal that contains fat to improve absorption since they dissolve in oil (5).
If you want to dissolve your multivitamin in water, the best way to do so is to pulverize them first. You can do this by using a mortar and pestle or a pill crusher (6). Crush no more than the daily recommended dose of your vitamin and grind the pills into a fine multivitamin powder to ensure that they mix into the water well. Of course, you are free to add this multivitamin powder to a shake, juice, or anything else you’d like to add it to in order to make it more palatable.

Why crush your pills when you can start with the effective and highly absorbable liquid multivitamin formulated for all?
"I give Liquid Daily to my daughter and she barely tastes it, even just added to water, which is great!"
- Olivia T.
"I give Liquid Daily to my daughter and she barely tastes it, even just added to water, which is great!"
- Olivia T.
Try Liquid Daily - the methylated liquid multivitamin packed with 20 essential vitamins & minerals.
BUY NOWVitamin Supplements’ Absorption
When it comes to vitamin supplements’ absorption, some vitamins do better than others. Centrum, for example, is known as a “bedpan pill,” meaning that it passes into the bedpan undisturbed and unabsorbed (7). This is incredibly unfortunate, especially for elderly patients who need essential micronutrients since they’re more likely to suffer from malnutrition or vitamin deficiencies (8).
How long does it take for vitamins to dissolve in your stomach? There is a test you can do to see how easily your tablets break down. This is the “acid test,” which involves placing a cup of white vinegar into a small bowl and keeping it consistently at 98 degrees by placing it in a larger bowl that you top up several times with warm tap water. You want to keep it close to 98 degrees for half an hour.
Drop your pill into the vinegar, and jostle it about every 5 minutes by gently shaking or swirling the cup. The tablet should dissolve within 30 minutes. If it doesn’t dissolve within a full hour, it’s not helping you. The website the acid test was found on recommends liquid vitamins for those whose vitamins didn’t break down (9). As a general rule, liquid vitamins (and anything that can be added to liquid, such as powders) have the best vitamin absorption.
Try Liquid Daily
Liquid Daily is the all-in-one liquid multivitamin that is nearly tasteless when added to any drink or juice!
- 18 Essential Vitamins & Minerals
- Advanced Liquid Absorption
- Zero sugars, fillers, or artificial flavorings
- Safe & Effective for Kids & Adults
Try Liquid Daily
Liquid Daily is the all-in-one liquid multivitamin that can be added to any drink or juice!
- 18 Essential Vitamins & Minerals
- Advanced Liquid Absorption
- Zero sugars, fillers, or artificial flavorings
- Safe & Effective for Kids & Adults!
How long does it take for multivitamins to leave your system? The answer is fairly complex. As we said earlier, there are water-soluble vitamins and fat-soluble ones. Fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K are stored in the liver, adipose/fat tissue, and skeletal muscle (10). Some say that water-soluble vitamins (B vitamins and vitamin C) can take 30 minutes to an hour to leave your system, whereas other sources say it can remain for up to 48 hours. Fat-soluble vitamins can remain in your system for 15 hours (11). Other sources say they can be stored in your body for up to 6 months (12).
Multivitamin absorption, therefore, can depend on a number of factors. The water-soluble vitamins are released relatively quickly, but the fat-soluble vitamins take more time. If you’ve got minerals in your vitamin as well, those have a slower absorption rate. Are you curious as to where vitamins are absorbed? The majority of vitamin absorption occurs in the small intestine (13). If you want more specific details on how to get optimal absorption for your vitamins, try Googling “vitamin absorption chart.” You’ll see a breakdown of which vitamins help with absorption and which ones hinder each other.
Dissolving Vitamins in Water
We’ve already talked about crushing vitamins for better absorption and the acid test, but did you know you can also try dissolving vitamin tablets in water to see how well they’d absorb into your body? Like the acid test, if they haven’t dissolved in 50 minutes, they’re likely not doing you much good. Of course, you can try dissolving vitamins in water and then drink your vitamins as well, but be aware: that method takes much longer than simply crushing them first.
At this point, you may be wondering, “Are minerals water or fat-soluble?” Again, the answer is complicated. Minerals travel through the body in different ways. Potassium is absorbed quickly into the bloodstream, where it circulates and is excreted by the kidneys, making it similar to a water-soluble vitamin. Calcium is more similar to a fat-soluble vitamin since it needs a carrier for absorption and transport.
Having too much of one major mineral can result in deficiency in another. Those imbalances can be caused by supplement overload or food sources. Eating too many processed or salty foods can result in calcium loss. This is because calcium binds with excess sodium in the body and is excreted when the body senses that sodium levels must be lowered. Taking too many phosphorus supplements can reduce your ability to absorb magnesium in a similar way (15).
Can I Dissolve Vitamin C in Water and Drink It?
By now, you should already know the answer to the question, “Can I dissolve vitamin C in water and drink it?” You can dissolve vitamin C tablets in water. Can you dissolve vitamin C in hot water, though? That’s a good question. Water-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins B and C) quickly degenerate once they’re heated (16).
If you’re curious what temperature destroys vitamin C, it can begin to denature at temperatures as low as 86 degrees Fahrenheit, and the negative effects of heat increase significantly at 140 degrees, even more at 170 degrees (17). This study we’re referring to here was done specifically to measure the denaturation of vitamin C in vegetables. Although supplement pills contain stabilizers (18) to ensure the vitamins are still viable at room temperature, we still recommend that you avoid using hot water to dissolve vitamin C if you can.
Does hot water destroy vitamin C in iron? People commonly use vitamin C and iron together because it’s believed to increase absorption (19). However, there is conflicting evidence regarding that, as a more recent study suggests that vitamin C is not necessary to increase iron absorption for those who are iron deficient (20). Either way, due to the data above, we recommend that you don’t use hot water for combination supplements such as those with iron and vitamin C, since the temperature of the water could decrease the effectiveness of vitamin C.
Powder Vitamins to Add to Water
Are you looking for powder vitamins to add to water? Supplements to add to water can be appealing for a number of reasons. First, they are more easily absorbed into your body than pills. Second, unlike liquid, they don’t need to be refrigerated to be shelf-stable. Third, you can add them to anything you’d like, whether it be juice, a morning smoothie, etc. Multivitamin powder for adults and kids can come in a variety of forms, including a big tub you scoop the powder from, and vitamin powder packets that are convenient when you’re on the go. We’ll offer a brief rundown on the top powder vitamins so you can find the best multivitamin powder for you.
Seeking Health Optimal Multivitamin Powder is one of the best multivitamin powders available today. It’s got vitamins A, C, D3, E, K2, along with a slew of B vitamins and minerals. Although many of the vitamins are above their daily recommended intake, the amounts don’t seem to reach the upper limit for vitamin intake. Some of the vitamins (such as B12) have no adverse effects, and thus, have no UL (21).
Unfortunately, many powder vitamins contain too much of a specific vitamin. As we touched on earlier, fat-soluble vitamins are stored in the body. For that reason, they’re more likely to cause toxicity (22). Some of the vitamin powders we found contained double the UL for fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin A, so we chose not to include them on this list. Always do your research before you choose your vitamin, and ask your doctor before taking any supplements.
Forever Beautiful Mix by yoursuper.com is a good option for women looking for a safe vitamin boost. It contains all certified organic foods and has a bit of iron, vitamin A, C, and E. It’s also got calcium, potassium, and magnesium. It’s not packed full of all the vitamins you need, but since it doesn’t have too much of any one vitamin, it’s a good option for those looking to supplement an already healthy diet without risking toxicity. Organic Superfoods Probiotics mix by Orgain is another option for men and women. It’s got some calcium, potassium, and iron in it to boost mineral levels.
References
- Bhogal, Ramneek S. “Are Liquid Vitamins Better Than Pills?” DaVinci Laboratories, 26 4 2019, https://blog.davincilabs.com/blog/are-liquid-vitamins-better-than-pills. Accessed 29 6 2021.
- Charlie, Ware. “Liquid or Pill Vitamin: Which is Better?” Healing Blends, 24 3 2020, https://healingblendsglobal.com/blogs/lifestyle/liquid-or-pill-vitamin-which-is-better. Accessed 29 6 2021.
- Arnarson, Atli. “The Water-Soluble Vitamins: C and B Complex.” Healthline, 3 11 2017, https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/water-soluble-vitamins. Accessed 29 6 2020.
- Clifford, J., and A. Kozil. “Fat-Soluble Vitamins: A, D, E, and K.” Colorado State University, 9 2017, https://extension.colostate.edu/topic-areas/nutrition-food-safety-health/fat-soluble-vitamins-a-d-e-and-k-9-315/. Accessed 29 6 2021.
- Fletcher, Jenna. “Is There a Recommended Time to Take Vitamins?” Medical News Today, 16 12 2019, https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/319556#fat-soluble-vitamins. Accessed 29 6 2021.
- Consumer Lab. “Home Test for Disintegration of Vitamins and Supplements.” ConsumerLab.com, ?, https://www.consumerlab.com/home-test/. Accessed 29 6 2021.
- Calton Nutrition. “5 Potential Problems with Your Multivitamin.” Calton Nutrition, 10 3 2020, https://www.caltonnutrition.com/5-potential-problems-with-your-multivitamin/. Accessed 29 6 2021.
- Larsen, Dana. “Why Seniors Have Different Nutritional Needs.” A Place for Mom, 17 12 2019, https://www.aplaceformom.com/caregiver-resources/articles/senior-nutritional-needs. Accessed 29 6 2021.
- CantonRep.com. “Do Your Vitamins Dissolve Quickly Enough to Be Absorbed Into Your System?” Canton Rep, 31 5 2011, https://www.cantonrep.com/article/20110531/BLOGS/305319960. Accessed 30 6 2021.
- Center for Ecogenetics and Environmental Health. Fat-Soluble Vitamins: The Good and the Bad. https://depts.washington.edu/ceeh/downloads/Fast Facts Fat Soluble Vitamins 063015.pdf. Environmental and Occupational Health Sciences at the University of Washington, ?
- McInnes, James, and Kritika Gupta. “How Long Do Vitamins Stay in Your System Before Your Body Goes Back to its Normal State?” Quora, 3 1 2020, https://www.quora.com/How-long-do-vitamins-stay-in-your-system-before-your-body-goes-back-to-its-normal-state-Vitamin-D-C-Zinc-Multi-vitamin. Accessed 30 6 2021.
- Galvin, Mary L. “Vitamins.” KidsHealth from Nemours, 7 2014, https://kidshealth.org/en/kids/vitamin.html. Accessed 6 30 2021.
- Bowen, Richard. “Absorption of Vitamins.” VIVO Pathophysiology, 11 2018, http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/digestion/smallgut/absorb_vitamins.html#:~:text=Essentially all vitamin absorption occurs in the small intestine. Accessed 30 6 2021.
- CantonRep.com. “Do Your Vitamins Dissolve Quickly Enough to Be Absorbed Into Your System?” Canton Rep, 31 5 2011, https://www.cantonrep.com/article/20110531/BLOGS/305319960. Accessed 30 6 2021.
- Harvard Health. “Vitamins and Minerals.” HelpGuide, 4 12 2018, https://www.helpguide.org/harvard/vitamins-and-minerals.htm. Accessed 30 6 2021.
- Spritzler, Franziska. “How Cooking Affects The Nutrient Content of Foods.” Healthline, 7 11 2019, https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/cooking-nutrient-content. Accessed 1 7 2021.
- Igwemmar, N. C., et al. “Effect of Heating on Vitamin C Content of Some Selected Vegetables.” International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, vol. 2, no. 11, 2013, pp. 209-212. ijstr.org, https://www.ijstr.org/final-print/nov2013/Effect-Of-Heating-On-Vitamin-C-Content-Of-Some-Selected-Vegetables.pdf. Accessed 1 7 2021.
- Charlie, Ware. “Liquid or Pill Vitamin: Which is Better?” Healing Blends, 24 3 2020, https://healingblendsglobal.com/blogs/lifestyle/liquid-or-pill-vitamin-which-is-better. Accessed 29 6 2021.
- Hurrell, Richard. “Iron Bioavailability and Dietary Reference Values.” National Library of Medicine, 5 2010, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20200263/. Accessed 1 7 2021.
- Manaker, Lauren. “You Don't Need Vitamin C with Your Iron Supplements, Study Suggests.” Very Well Health, 12 11 2020, https://www.verywellhealth.com/vitamin-c-iron-supplement-study-5087131. Accessed 1 7 2021.
- Kubala, Jillian. “Can You Overdose on Vitamins?” Healthline, 20 1 2020, https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/can-you-overdose-on-vitamins. Accessed 1 7 2021.
- Center for Ecogenetics and Environmental Health. Fat-Soluble Vitamins: The Good and the Bad. https://depts.washington.edu/ceeh/downloads/Fast Facts Fat Soluble Vitamins 063015.pdf. Environmental and Occupational Health Sciences at the University of Washington. Accessed 1 7 2021.
More articles from Better Family